Porcelain Veneers: The Ultimate Solution for Tetracycline-Stained Teeth
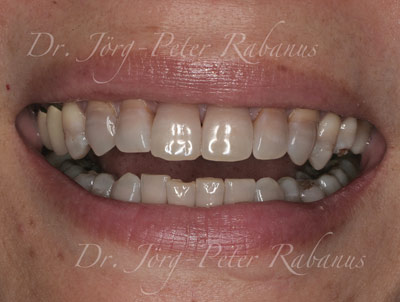
Tetracycline-stained teeth are a unique challenge in cosmetic dentistry. These stains, caused by exposure to tetracycline antibiotics during tooth development, result in discolorations that range from yellow to dark brown or even gray. Unlike surface stains, tetracycline stains are deeply embedded in the tooth structure, making them resistant to conventional whitening methods. For those seeking a permanent and aesthetic solution, porcelain veneers stand out as the best option.
Understanding Tetracycline-Stained Teeth
Tetracycline stains occur during odontogenesis, the process of tooth development, when tetracycline binds to calcium in the developing teeth. This leads to discolorations that are:
Deeply ingrained: The stains are not superficial and cannot be removed through surface treatments like bleaching.
Variable in appearance: The severity and color of the stains can differ, ranging from faint yellow bands to severe gray discolorations.
Associated with enamel issues: Tetracycline-stained teeth often have thin or compromised enamel, which can affect both aesthetics and structural integrity.
These characteristics make tetracycline stains particularly difficult to treat with traditional cosmetic dental methods.
Why Porcelain Veneers Are the Best Solution
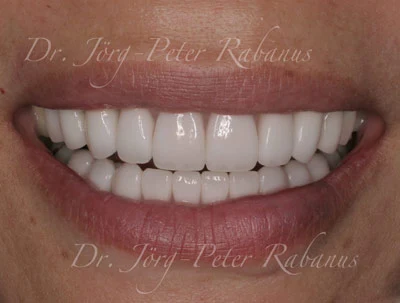
Porcelain veneers are a transformative option for patients with tetracycline-stained teeth. Unlike bleaching or other surface treatments, veneers provide a permanent, customizable solution that masks deep discolorations while enhancing overall aesthetics. Here’s why they are the gold standard:
1. Comprehensive Coverage
Porcelain veneers are thin shells of dental porcelain that are bonded to the front surface of the teeth. They completely cover the discolored areas, effectively masking even the darkest stains. This ensures a uniform and natural-looking appearance.
2. Customizable Aesthetics
Dental porcelain comes in a wide range of opacities and translucencies, allowing cosmetic dentists to tailor veneers to the individual’s needs. For tetracycline-stained teeth, veneers can:
Block underlying discoloration with precise opacity.
Mimic the natural translucency and texture of teeth.
Achieve a desired shade that complements the patient’s complexion.
3. Preservation of Tooth Structure
Compared to crowns, which require significant reduction of the tooth, veneers are a conservative option. They involve minimal removal of tooth structure, preserving as much natural enamel as possible. This is particularly important for tetracycline-stained teeth, which may already have compromised enamel.
However, depending on the severity of the staining, the level of tooth preparation for porcelain veneers needs to be adjusted, depending on the desired outcome. It is still much more conservative than porcelain crowns:
4. Durability and Longevity
Porcelain veneers are durable and resistant to staining, ensuring that the results are long-lasting. With proper care, veneers can maintain their appearance for 10-15 years or more, making them a worthwhile investment.
Why Whitening May Not Work
While dental bleaching can be effective for surface stains or mild discolorations, it often fails with tetracycline-stained teeth. This is due to the nature of the stains, which are:
Locked into the tooth structure: The pigments from tetracycline are incorporated during development and cannot be lifted with hydrogen peroxide or other whitening agents.
Non-uniform: Even if some improvement is achieved, the result is often uneven, leaving the teeth with visible bands or patches.
The Treatment Process for Veneers
For patients with tetracycline-stained teeth, the veneer process involves:
Consultation and Planning: A thorough examination and discussion of aesthetic goals.
Preparation: Minimal enamel removal to create space for the veneers.
Shade Matching: Selecting the right combination of opacity and translucency to achieve a natural look.
Fabrication: Custom veneers are crafted to fit perfectly and match the desired appearance.
Bonding: The veneers are permanently bonded to the teeth, transforming the smile.
Advantages Over Other Options
Porcelain veneers provide benefits that other treatments cannot match:
Immediate Results: Unlike whitening, which requires multiple sessions and may not achieve satisfactory outcomes, veneers deliver instant improvements.
Uniform Appearance: They eliminate the unevenness often associated with tetracycline stains.
Natural Look: Modern veneers are designed to look realistic, avoiding the “fake” appearance some associate with cosmetic dentistry.
Conclusion:
Tetracycline-stained teeth can have a profound impact on a person’s confidence and self-esteem. While traditional methods like whitening may fall short, porcelain veneers offer a reliable and aesthetically pleasing solution. By masking deep discolorations and enhancing the natural beauty of the teeth, veneers allow patients to smile with confidence and pride. If you’re seeking a transformative treatment for tetracycline-stained teeth, porcelain veneers are undoubtedly the best option.
References:
Maxillary rehabilitation of tetracycline-stained teeth with diastemas by using ceramic veneers and a digital workflow.
Turkyilmaz I et al. J Dental Sci 2023; 18(3): 1425-1426.
A review on natural teeth whitening.
Benahmed AG et al. J Oral Bioscience 2022; 64(1): 49-58.
Conservative approach to treating severe tetracycline staining: a 12-month follow-up.
Santos Rocha R et al. Gen Dentistry 2021; 69(4): 41-44.
Effect of ceramic materials on the optical properties of porcelain veneers for tetracycline-stained teeth.
Chen J et al. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2021; 39(3): 341-346.
Severe tetracycline dental discoloration: Restoration with conventional feldspathic ceramic veneers. A clinical report
Faus-Matoses V et al. Clin Exp Dentistry 2017; 9(11): e1379-e1382.
A Restorative Challenge: Tetracycline-Stained Teeth
Cutbirth ST. Dentistry Today 2015; 34(7): 126, 128-30.
A case report of a 20-year clinical follow-up of porcelain laminate veneer restorations
Katoh Y et al. Operative Dentistry 2009; 34(5): 626-30.
Clinical considerations in managing severe tooth discoloration with porcelain veneers
Chu FCS. J Am Dental Assoc 2009; 140(4): 442-6.
Restoring tetracycline-stained teeth with a conservative preparation for porcelain veneers: case presentation
Bassett J et al. Pract Proced Aesthetic Dentistry 2004; 16(7): 481-486.
Severe tetracycline dental discoloration: Restoration with conventional feldspathic ceramic veneers. A clinical report.
Faus-Llacer V et al. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dentistry 2017; 9(11).
Nonvital tooth bleaching: a review of the literature and clinical procedures.
Plotino G et al. J Endod 2008; 34(4): 394-407.
Restoring the Tetracycline Stained Dentition -Blocking out discolored dentin while mimicking the natural tooth structure.
Wynne T. Inside Dentistry October 2016; 56-61.



