Porcelain veneers have become a prime treatment modality for smile designs. They are the most popular tools for creating smile makeovers.
Dental veneers change a smile fast and dramatically and may remain in your mouth just as long as your natural teeth if done by an experienced cosmetic dentist. One indication of a level of excellence in the area of cosmetic dentistry and smile designs is a dentist who is accredited by the American Academy of Cosmetic Dentistry.
Direct or indirect veneers are bonded to natural tooth surfaces, either enamel or dentin, depending on the degree of dental wear and the degree of necessary correction of tooth color, tooth position, and attrition/wear of tooth structure. Bonded veneers help to preserve tooth structure while adding strength to the underlying tooth structure by being intimately connected to a tooth and protecting against any possible invasion by decay-causing microorganisms.
The patients below illustrate dramatic improvements that can be obtained with porcelain veneers. Not much tooth structure needed to be removed to create these natural smile makeovers. The greatest concern of patients who are looking to improve their smiles with veneers is the degree of tooth reduction necessary. Evidently, we practice minimally-invasive dentistry, but the degree of tooth reduction depends on various parameters, such as the condition of the current dental condition and the degree of desired and necessary changes. Dr. Jorg-Peter Rabanus discussed this concern in detail on his YouTube Channel: Porcelain Veneers: Tooth Reduction


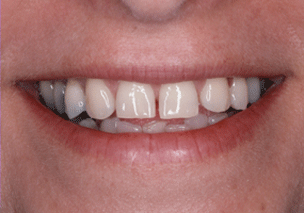
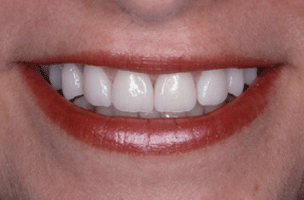
Indirect Porcelain Veneers vs. Direct Composite Veneers: A Comparative Analysis
In the realm of cosmetic dentistry, veneers have become an increasingly popular solution for enhancing the appearance of teeth. They offer a minimally invasive method to correct aesthetic imperfections such as discoloration, chips, cracks, and misalignments. The two most common types of veneers are indirect porcelain veneers and direct composite veneers. While both options provide excellent results, they differ in terms of materials, application processes, longevity, cost, and overall patient experience. Here we will compare and contrast indirect porcelain veneers and direct composite veneers, highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages.
1. Material Composition and Aesthetic Quality
The primary distinction between indirect porcelain veneers and direct composite veneers lies in the material used. Porcelain is a ceramic material known for its durability, translucency, and natural appearance. Porcelain veneers are crafted in a dental laboratory, where skilled technicians design and fabricate the veneers based on precise molds of the patient’s teeth. This allows for a high level of customization, ensuring that the veneers match the natural color and texture of the surrounding teeth. Porcelain veneers also mimic the way light reflects off natural teeth, making them one of the most aesthetic options in cosmetic dentistry.
On the other hand, composite resin is a tooth-colored plastic material that can be directly applied to the teeth during the appointment with the cosmetic dentist. Composite veneers are molded and shaped by the esthetic dentist to fit the patient’s teeth, and then hardened using a monochromatic blue light. While modern composite materials have improved significantly in terms of strength and appearance, they generally do not achieve the same level of aesthetic quality as porcelain. Composite veneers may reflect light differently, which can make them less natural-looking in certain lighting conditions.
2. Procedure and Treatment Time
The application process for indirect porcelain veneers and direct composite veneers varies significantly. Indirect porcelain veneers typically require two or more dental appointments. During the first visit, the dentist will prepare the teeth by removing a thin layer of enamel and taking impressions. These impressions are sent to a dental laboratory, where the porcelain veneers are custom-made to fit the patient’s teeth. Once the veneers are ready, the patient returns for the second appointment, during which the veneers are bonded to the teeth using a strong adhesive.
In contrast, direct composite veneers can usually be completed in a single visit. The dentist begins by cleaning and slightly roughening the surface of the teeth to ensure better adhesion. Then, the composite resin is applied in layers, sculpted into shape, and cured with a light. Because the procedure is less time-consuming and does not require laboratory work, direct composite veneers are often seen as a more convenient option for patients seeking a quicker solution.
3. Durability and Longevity
In terms of longevity, indirect porcelain veneers are generally considered more durable than direct composite veneers. Porcelain is a highly resilient material that is, if bonded properly resistant to staining, chipping, and wear. With proper care, porcelain veneers can last 10 to 15 years or longer, making them a long-term investment for patients seeking a lasting cosmetic improvement.
Direct composite veneers, while strong, are more prone to wear and staining over time. The material is softer compared to porcelain, meaning it can chip or become scratched more easily. Composite veneers may require touch-ups or replacement after 5 to 7 years, depending on the patient’s oral hygiene habits and lifestyle choices. Additionally, composite veneers tend to stain more easily from foods and beverages like coffee, wine, and tobacco, requiring more maintenance to keep them looking fresh.
4. Cost Considerations
Cost is an important factor when choosing between indirect porcelain veneers and direct composite veneers. Indirect porcelain veneers are more expensive due to the labor-intensive process involved in creating custom-made veneers in a dental laboratory. The cost typically ranges from $1,500 to $3,000 per tooth, depending on the complexity of the case, the dental office, and geographic location. However, given their longevity and durability, porcelain veneers may be seen as a more cost-effective option in the long run.
In contrast, direct composite veneers are less expensive, yet often still ranging from $1,250 to $2,000 per tooth when delivered in cities with high standards, expectations, and cost of living, such as San Francisco or New York City. Since the procedure can be completed in a single visit and does not require laboratory work, the cost is significantly lower. For patients seeking a more affordable option or those with budget constraints, composite veneers may be an attractive choice. However, it is important to consider that the shorter lifespan of composite veneers may lead to additional costs for replacements or repairs over time.
5. Conservation of Tooth Structure
One of the advantages of direct composite veneers is that they require minimal removal of tooth structure. The dentist only needs to slightly roughen the surface of the tooth to ensure proper adhesion of the composite resin. In many cases, no significant enamel reduction is necessary, which makes composite veneers a more conservative option for patients who wish to preserve as much of their natural tooth as possible.
Indirect porcelain veneers, on the other hand, generally require more tooth preparation. A small amount of enamel is typically removed to accommodate the thickness of the veneer and ensure a secure bond. While this removal is minimal, the amount of tooth structure removed for each case depends on the initial condition of the natural teeth and the desired outcome. If the desired changes are drastic, such as a correction of crowded teeth, the rehabilitation of worn teeth, and the rejuvenation of severely stained teeth towards a much lighter shade, more tooth structure needs to be removed to conceal the underlying tooth structure.
6. Repairs and Maintenance
If a veneer becomes damaged, direct composite veneers are easier and less expensive to repair. The dentist can typically replace or touch up small chips or cracks by adding more composite resin and polishing it to match the rest of the veneer. This can often be done in a single appointment.
Indirect porcelain veneers, however, are more difficult and costly to repair. If a porcelain veneer chips or cracks, it may need to be replaced entirely. While the material is durable, once damaged, porcelain veneers may require more extensive and expensive repairs compared to composite veneers.
Conclusion
Both, indirect porcelain veneers and direct composite veneers, offer unique advantages and limitations, and the choice between them depends on various factors such as budget, desired aesthetic outcome, treatment time, and long-term goals. Porcelain veneers excel in terms of durability, aesthetics, and longevity, making them an excellent choice for patients looking for a long-term solution to enhance their smile. However, they come at a slightly higher cost and require more extensive tooth preparation.
On the other hand, composite veneers provide a insignificantly more affordable and less invasive option with quicker results, but they may not offer the same level of aesthetic quality or durability as porcelain. Patients who are looking for a more temporary solution or are on a budget may find composite veneers to be a more suitable choice. Ultimately, the decision should be based on a careful consideration of the patient's needs, lifestyle, and goals, in consultation with a skilled cosmetic dentist, such as someone who is accredited by the American Academy of Cosmetic Dentistry (AACD).
Despite being the most popular treatment modality of cosmetic dentistry, direct and indirect dental laminates made of various ceramics and composites are not the only way to improve the appearance of your teeth and your smile. You will find additional information on the following pages:
- Teeth Whitening
- Dental Bonding
- Dental Implants
- Invisible Fillings
- Orthodontics, such as Invisalign and Braces
- Tooth Contouring and Reshaping
These procedures are often used in combination with each other.
These procedures are often used in combination with each other.
Ask Dr. Rabanus personally via his direct E-Mail.
Find additional smile designs with porcelain veneers at our additional smile gallery.



